-
Posts
24,612 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
834
Everything posted by Barand
-
You are inserting seven values into six columns. Don't insert the user_id, let the auto_increment take care of that.
-
Confusion? If they can't work out where other members' names are, having seen where their name is located, then they are beyond any help we might offer. You should leave it where it is as an initiative test for site membership.
-
That will give something like ... HAVING COUNT(1) = count(3) What you want is ... HAVING COUNT(1) = 3
-
SELECT product , MAX(timestamp) as lastsale FROM inventory GROUP BY product ORDER BY lastsale DESC LIMIT 4
-

I need urgent help with my prepare statement!
Barand replied to Jimmy_jolling's topic in PHP Coding Help
Read the manual. store_result() returns boolean, not a result object. -
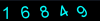
try $chars = '16849'; $im = imagecreate(500,100); $bg = imagecolorallocate($im,0,0,0); $fg = imagecolorallocate($im,0,0xFF,0xFF); for ($c=0; $c<5; $c++) { $angle = $c*10; $ch = $chars[$c]; imagettftext($im, 60, $angle, $c*100+10, 90, $fg, 'c:/windows/fonts/Arial.ttf', $ch); } header("Content-type: image/png"); imagepng($im); imagedestroy($im);
-
Perhaps $listingFee = ''; foreach ($xml->Fees->Fee as $fee) { if ($fee->Name=='ListingFee') { $listingFee = sprintf('%0.2f%s', $fee->Fee, $fee->Fee['currencyID']); } } echo $listingFee; //--> 0.25USD
-

line breaks from textarea to database and then to display
Barand replied to Fostav's topic in PHP Coding Help
Leave the line breaks in the text when saving to the database. If outputting to a text area then leave the breaks as they are. If outputting to to other parts of a page, use nl2br($text) to add <br> to the line breaks. -

nothing happens when I click the submit button to insert
Barand replied to ricky15's topic in PHP Coding Help
I suspect that is the result of putting a forum code tag in the middle of the code -
Setting a variable $return_value does not return the value. function get_query_value ($con,$query){ $con->real_query($query); $result=$con->use_result(); $row=$result->fetch_row(); $result->close(); return $row[0]; //<---- return the value } @ginerjm - the function is closing the result set, NOT the connection.
-
A couple of other things. Avoid the use of "global", pass the connection to the function. You are wasting resources by using several queries, each fetching only a single column. You can do everything in a single query. function predictor ($con, $home_team, $away_team) { $sql = "SELECT IFNULL(home_team_strength * away_team_strength / home_strength, 0) as result0 , IFNULL(away_team_strength_2 * home_team_defence / away_strength, 0) as result1 FROM ( SELECT AVG(IF(home_team = ?, HTgoals, null)) as home_team_strength , AVG(IF(home_team = ?, ATgoals, null)) as home_team_defence , AVG(IF(away_team = ?, HTgoals, null)) as away_team_strength , AVG(IF(away_team = ?, ATgoals, null)) as away_team_strength_2 FROM results ) team CROSS JOIN ( SELECT AVG(HTgoals) as home_strength , AVG(ATgoals) as away_strength FROM results ) league;"; $stmt = $con->prepare($sql); $stmt->execute( [ $home_team,$home_team,$away_team,$away_team ] ); return $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_NUM); }
-
Your get_query_value() function does not return anything
-
Use code tags and put it in a legible format, and then someone may look at the problem for you
-
imagepng imagepng($dst, 'path/to/file');
-
Test data mysql> select * from seizoen16; +--------------+--------+----------+----------------+--------+ | seizoen16_id | speler | gespeeld | honderdtachtig | punten | +--------------+--------+----------+----------------+--------+ | 1 | Fred | 20 | 8 | 40 | | 2 | Peter | 20 | 10 | 56 | | 3 | Paul | 22 | 15 | 63 | | 4 | Mary | 21 | 9 | 56 | +--------------+--------+----------+----------------+--------+ SELECT cast(rank as char) as rank , speler , gespeeld , honderdtachtig , punten FROM ( SELECT speler , gespeeld , honderdtachtig , @row :=@row+1 as row , @rank := IF(punten = @lastpunten, @rank, @row) as rank , @lastpunten := punten as punten FROM seizoen16 JOIN (SELECT @row:=0, @rank:=0, @lastpunten:=0) init ORDER BY punten DESC ) points +------+--------+----------+----------------+--------+ | rank | speler | gespeeld | honderdtachtig | punten | +------+--------+----------+----------------+--------+ | 1 | Paul | 22 | 15 | 63 | | 2 | Peter | 20 | 10 | 56 | | 2 | Mary | 21 | 9 | 56 | | 4 | Fred | 20 | 8 | 40 | +------+--------+----------+----------------+--------+
- 1 reply
-
- 1
-

-

how to credit commisions to all the parents of a child php mysql
Barand replied to mrcgoud's topic in PHP Coding Help
This should get you on your way. If your tables are like these mysql> SELECT * FROM plan; +---------+--------+------------------+ | plan_id | amount | daily_commission | +---------+--------+------------------+ | 1 | 100 | 0.70 | | 2 | 250 | 1.00 | | 3 | 500 | 1.50 | | 4 | 1000 | 2.00 | +---------+--------+------------------+ mysql> select * from user; +---------+----------+---------+-------------+--------+ | user_id | password | plan_id | referred_by | status | +---------+----------+---------+-------------+--------+ | 1 | 22222 | 1 | NULL | 1 | | 2 | 12345 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | 3 | 123sad | 1 | 2 | 1 | | 4 | asdf4f | 2 | 3 | 1 | | 5 | 321423 | 4 | 2 | 1 | +---------+----------+---------+-------------+--------+ CREATE TABLE `income` ( `inc_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `amount` decimal(8,2) DEFAULT NULL, `income_date` date NOT NULL, `income_type` char(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'D' COMMENT '(D)aily or (R)eferral', PRIMARY KEY (`inc_id`) ) ; A query like this one, run daily, will create the daily commission income records INSERT INTO income (user_id,income_date,amount,income_type) SELECT u.user_id , CURDATE() , p.amount * p.daily_commission / 100 , 'D' FROM user u INNER JOIN plan p USING (plan_id); To calculate the referral commissions you will need a recursive function to climb the parent tree. Here's an example $db = pdoConnect($db1); /********************************************************************* * USER TEST DATA **********************************************************************/ $referrer = '6'; $plan = 1; $password = 'secret'; /********************************************************************* * ADD USER **********************************************************************/ $pass_hash = password_hash($password, PASSWORD_BCRYPT); $usersql = "INSERT INTO user (password, plan_id, referred_by) VALUES (?,?,?)"; $userstmt = $db->prepare($usersql); $userstmt->execute( [ $pass_hash, $plan, $referrer ] ); /********************************************************************* * GET THE PLAN AMOUNT 10% COMMISSION **********************************************************************/ $plansql = "SELECT amount FROM plan WHERE plan_id = ?"; $planstmt = $db->prepare($plansql); $planstmt->execute( [$plan] ); $row = $planstmt->fetch(); $commission = $row['amount'] * 0.1; // 10% commission /********************************************************************* * ADD 10% COMMISSION TO REFERRER INCOME **********************************************************************/ $incomesql = "INSERT INTO income (user_id, amount, income_date, income_type) VALUES (?,?,CURDATE(),'R')"; $incomestmt = $db->prepare($incomesql); $incomestmt->execute( [ $referrer, $commission ] ); /********************************************************************* * ADD 5% COMMISSION TO REFERRER'S REFERRERS' INCOMEs **********************************************************************/ $refsql = "SELECT referred_by FROM user WHERE user_id = ?"; $refstmt = $db->prepare($refsql); $commission /= 2; // 5% commission addCommission ($referrer, $commission, $refstmt, $incomestmt); /********************************************************************* * RECURSIVE FUNCTION TO FIND ALL REFERRERS AND ADD COMMISSION **********************************************************************/ function addCommission ($referrer, $commission, $refstmt, $incomestmt) { $refstmt->execute( [$referrer] ); $row = $refstmt->fetch(); if ($row && $row['referred_by'] != null) { $incomestmt->execute( [ $row['referred_by'], $commission ] ); addCommission ($row['referred_by'], $commission, $refstmt, $incomestmt); } } Don't store passwords as plain text. See the use of password_hash() in the above example. You would verify the password with password_verify() -

how to credit commisions to all the parents of a child php mysql
Barand replied to mrcgoud's topic in PHP Coding Help
My advice is to remove those amounts from the user table. The plan_amount should only be in the "plan" table, not duplicated for every user with that plan. There should be a separate "income" table (user, date, amount) to which you add a record each time commission is paid. -
Use forward slashes. It saves having to worry about escaping backslashes (and quotes) and it's fine on Windows as well as Linux. define('MYSQL','d:/wamp/www/');
-
Both these will do it $serialno = strstr($filename, '_', true); // get chars before the '_' $serialno = substr($filename, 0, 4); // get first four chars
-
And remove the quotes from 'ASC'. (As the default is ASC you don't really need it.) SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY id
-
You might find it better to load the file into the database then use the form to edit the database
-
To illustrate the above, if you have mysql> SELECT * FROM tbl_bookings; +------------+------+-----+--------+------------+------+--------+ | booking_id | room | day | week | session_no | user | class | +------------+------+-----+--------+------------+------+--------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 201640 | 1 | ABC | CLASS1 | | 2 | 1 | 1 | 201640 | 2 | DEF | CLASS2 | | 3 | 1 | 1 | 201640 | 4 | GHI | CLASS3 | | 4 | 1 | 1 | 201640 | 5 | JKL | CLASS4 | +------------+------+-----+--------+------------+------+--------+ mysql> SELECT * FROM session; +------------+----------+----------+ | session_no | starts | ends | +------------+----------+----------+ | 1 | 09:30:00 | 10:29:59 | | 2 | 10:30:00 | 11:29:59 | | 3 | 11:30:00 | 12:29:59 | | 4 | 13:30:00 | 14:29:59 | | 5 | 14:30:00 | 15:29:59 | +------------+----------+----------+ Then you can find unfilled sessions like this SELECT s.session_no , s.starts , s.ends , b.room , b.user , b.class FROM session s LEFT JOIN tbl_bookings b ON s.session_no = b.session_no AND week = '201640' AND day = 1; +------------+----------+----------+------+------+--------+ | session_no | starts | ends | room | user | class | +------------+----------+----------+------+------+--------+ | 1 | 09:30:00 | 10:29:59 | 1 | ABC | CLASS1 | | 2 | 10:30:00 | 11:29:59 | 1 | DEF | CLASS2 | | 3 | 11:30:00 | 12:29:59 | NULL | NULL | NULL | <-- unfilled session | 4 | 13:30:00 | 14:29:59 | 1 | GHI | CLASS3 | | 5 | 14:30:00 | 15:29:59 | 1 | JKL | CLASS4 | +------------+----------+----------+------+------+--------+
-
Create you own topic. Don't just tack your question on the end of someone else's. EDIT: You have $_POST['username'] but the form field has name='name'
-
The first thing you need to do is break up that compound period column - you have three items in there that should be in separate columns Day number (1 - 7) Week (YYYYWW) Session number You will also need a session table containing five rows, one for each session 1 - 5. Your query needs to know what should be there if it wants to show you what is missing.
-
In your other topic I showed you how to read the files and pick out the numbers and text. However you have now changed the format of that file to make it much more difficult. You also wanted to write that file to a database table and now you want to put it in a form. When you have made up your mind exactly what you do want, let us know. After all, you don't want to waste any more of our time, do you?