-
Posts
24,615 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
835
Everything posted by Barand
-
With Firefox you can right click on the page and "Save as...". With Edge, ???
-
I totally agree with @requinix regarding the two tables. However, if you are willing to compromise over the output, you could do something like this SELECT uid , name , SUM(CASE payment_type WHEN 'cash' THEN payment ELSE 0 END) as cash , SUM(CASE payment_type WHEN 'card' THEN payment ELSE 0 END) as card , cost , cost-SUM(payment) as balance FROM payment GROUP BY uid +------+------+------+------+------+---------+ | uid | name | cash | card | cost | balance | +------+------+------+------+------+---------+ | 1 | kim | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | | 2 | lee | 95 | 0 | 95 | 0 | | 3 | kent | 50 | 50 | 100 | 0 | | 4 | iya | 40 | 20 | 80 | 20 | +------+------+------+------+------+---------+ If you really need every transaction listed, the SQL becomes quite complex involving user variables and subqueries. It would be much easier to do in the PHP as you output each row. [EDIT] ... For the sake of completeness SELECT uid , name , cash , card , cost , cost-total as balance FROM ( SELECT name , CASE payment_type WHEN 'cash' THEN payment ELSE 0 END as cash , CASE payment_type WHEN 'card' THEN payment ELSE 0 END as card , cost , @tot := CASE @previd WHEN uid THEN @tot + payment ELSE payment END as total , @previd := uid as uid FROM ( SELECT * FROM payment ORDER BY uid ) sorted JOIN (SELECT @previd:=0, @tot:=0) initialize ) recs; +------+------+------+------+------+---------+ | uid | name | cash | card | cost | balance | +------+------+------+------+------+---------+ | 1 | kim | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | | 2 | lee | 95 | 0 | 95 | 0 | | 3 | kent | 50 | 0 | 100 | 50 | | 3 | kent | 0 | 50 | 100 | 0 | | 4 | iya | 40 | 0 | 80 | 40 | | 4 | iya | 0 | 20 | 80 | 20 | +------+------+------+------+------+---------+
-
Variable names! while($rows = $resultset->fetch_assoc()) ^^^^ { echo "<option value='{$row[course_name]}'>{$row['course_name']}</option>"; ^^^ ^^^ } And the value should be the course_id
-
You don't have to create a web page on an iPad to be able to view it in a browser on an iPad
-
In future, use the <> button in the toolbar when posting code. (I've done it for you this time) In your query SELECT exam_time ,count() FROM test_booking_confirm WHERE DATEDIFF('exam_date',DATE_FORMAT('"+$date+"','%m-%d-%Y'))=0 GROUP BY exam_date,exam_time HAVING count()>1 the WHERE clause is FUBAR. when storing or working with dates in a db the format should be yyyy-mm-dd (DATE type) in PHP, the concatenation operator is a "." and not a "+" column names should not be in single quotes user-provided data should not be put directly into the query, used prepared statements Assuming the exam_date is the correct DATE type and format, make sure $date is the correct format EG $date = date('Y-m-d'); $stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT exam_time FROM test_booking_confirm WHERE exam_date = ? GROUP BY exam_date,exam_time HAVING count(*)>1 "); $stmt->bind_param('s', $date); $stmt->execute(); $stmt->bind_result($exam_time); $slots=array(); while($stmt->fetch { $slots[] = $exam_time; } But, personally, I'd look for slots with a count < 2 and just display those available.
-
@KHS I agree that SELECT * should not be used, but those "rows" you mentioned are "columns".
-
Don't use deprecated html markup, such as font color. Use style attribute. echo "<p style='font-size:4pt; color:#ffffff'>$echo</p>"; or define a class for those links in your css .mylink { font-size: 4pt; color: #FFFFFF; } then echo "<p class='mylink'>$echo</p> NOTE: I have no way of knowing what $echo contains. If it contains <a> tag then the styling will need to be applied there and not to the <p>
-
Take $values out of the subject
-
Your script needs a "base time" - the time from which you are counting. Instead of always starting your timer from 00:00:00 you would first calculate the time elapsed from the base time and start from there. EG base time = 09:00, and it is now 11:10:35, so your timer should start from "02:10:35" when it loads. If you next open the page at midday then the timer shoud start from "03:00:00"
- 5 replies
-
- javascript js
- timer
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
Input fields also work better when they have "name" attributes
-
1. As you are putting multiple names in the message it doesn't make sense to include (one of) them in the subject. 2. Your while loop should be while ($values = mysqli_fetch_array($result)) { otherwise you trash the $msg variable by overwriting it.
-

Server segfault's when trying to PDO::rollBack() ...
Barand replied to PatRoy's topic in PHP Coding Help
Autocommit! Yes, that's the whole idea behind transactions and committing or rolling back . try public function multiInsert($data) { $errorList = []; $stmt = $this->conn->prepare("INSERT INTO user (username, email, passwd) VALUES (?,?,?)"); foreach ($data as $rec) { try { $stmt->execute($rec); } catch (PDOException $ex) { $errorList[] = [ $rec, $ex->errorInfo[1], $ex->getMessage() ]; } } return $errorList; } -

Server segfault's when trying to PDO::rollBack() ...
Barand replied to PatRoy's topic in PHP Coding Help
Don't set autocommit to false. BeginTransaction will cancel it for the duration of the transaction until a commit or rollback is called. Don't commit every insert, do one commit after all the inserts are executed (or rollback if there was an exception) Don't save plaintext passwords. Use password_hash() and password_verify() I have rewritten your code (working, for me at any rate) <?php class wrapper { private $conn; public function __construct($con) { $this->conn = $con; } public function multiInsert($data) { $this->conn->beginTransaction(); try { $stmt = $this->conn->prepare("INSERT INTO user (username, email, passwd) VALUES (?,?,?)"); foreach ($data as $rec) { $stmt->execute($rec); } $this->conn->commit(); } catch (PDOException $e) { $this->conn->rollback(); throw $e; } } } const HOST = 'localhost'; const USERNAME = '...'; const PASSWORD = '...'; const DBNAME = '...'; // PDO database connection // $dsn = "mysql:dbname=".DBNAME."; host=".HOST."; charset=utf8"; $db = new pdo($dsn, USERNAME, PASSWORD, [ PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE => PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION, PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES => false, PDO::ATTR_DEFAULT_FETCH_MODE => PDO::FETCH_ASSOC ]); $data = array ( array ( "jdoe1", "[email protected]", "abc1"), array ( "jdoe2", "[email protected]", "abc2"), array ( "jdoe3", "[email protected]", "abc3"), array ( "jdoe4", "[email protected]", "abc4"), array ( "jdoe5", "[email protected]", "abc5"), ); $wrap = new wrapper($db); $wrap->multiInsert($data); /* RESULTS mysql> select * from user; +--------+----------+----------------+--------+ | userid | username | email | passwd | +--------+----------+----------------+--------+ | 1 | jdoe1 | [email protected] | abc1 | | 2 | jdoe2 | [email protected] | abc2 | | 3 | jdoe3 | [email protected] | abc3 | | 4 | jdoe4 | [email protected] | abc4 | | 5 | jdoe5 | [email protected] | abc5 | +--------+----------+----------------+--------+ */ ?> -
As an aside, is there a good administrative front-end for PostgreSQL (MySQL Workbench equivalent - modelling, admin, editing etc)?
-
If you are going to have a column for sequencing, take a tip from someone who used to program on paper then have their lines of code transferred to punch cards - sequence in increments of, say, 100 and not 1. That leaves lots of room to alter the sequence or add inserts.
-
Also, change the order of the code in your page, putting the php section first. Code flow should be something like this if POST data exists Validate data storing error messages if no errors do updates header("location: #") // reload page exit end if end if if GET data process GET data endif any other code necessary for building page e.g. menus !DOCTYPE html html output any validation error messages form form fields end form end html
- 3 replies
-
- form validation
- $_post variables
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with:
-
Nearly - you need to test $del[$key], not just $del
-
E.G. $res = $conn->query("SELECT i.model_id , i.model_name , c.category_id as cat_id , c.model_category_name as cat_name FROM model_index i JOIN models_category_ids USING (model_id) JOIN models_category c USING (category_id) "); $data = []; foreach ($res as $r) { if (!isset($data[$r['model_id']])) { $data[$r['model_id']] = [ 'name' => $r['model_name'], 'cats' => [] ]; } $data[$r['model_id']]['cats'][$r['cat_id']] = $r['cat_name']; } /* $data = Array ( [1] => Array ( [name] => John Doe [cats] => Array ( [1] => IT Devloper [3] => Mechanic ) ) [2] => Array ( [name] => Laura Norder [cats] => Array ( [2] => Photographer ) ) ) */
-
The link in your code is to the model_id Add "i.model_id" to the selected columns in the query, then the output will have $model->model_id If you need individual category_ids, revert your query to that getting several rows for each model and store the results in an array, indexed by model, so each model has an array of categories.
-
My query returns two output columns model_name cats Try echo model->model_name . " " . $model->cats . "<br>"; (of course, without seeing the code that actually runs the query and gets the results, that's just a guess.)
-
Which is line 19?
-
One way is with GROUP_CONCAT() SELECT i.model_name , GROUP_CONCAT(c.category_id,' ',c.model_category_name SEPARATOR ', ') as cats FROM model_index i JOIN models_category_ids USING (model_id) JOIN models_category_tbl c USING (category_id) GROUP BY i.model_id;
-
... or as you are using mysqli, put this line before your connection creation mysqli_report(MYSQLI_REPORT_ERROR|MYSQLI_REPORT_STRICT);
-
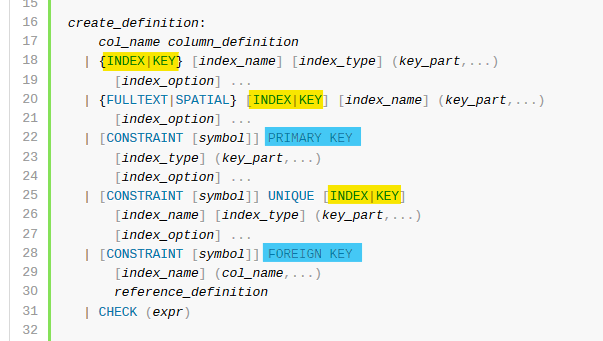
Below is an extract from the mysql reference manual As you can see, with the exceptions of "PRIMARY KEY" and "FOREIGN KEY" (which can be considered to be reserved phrases) the terms "index" and "key" are interchangeable.